Synchronous Reluctance Motors Technology
We will provide you with IE5 synchronous reluctance high-efficiency motor and drive solutions
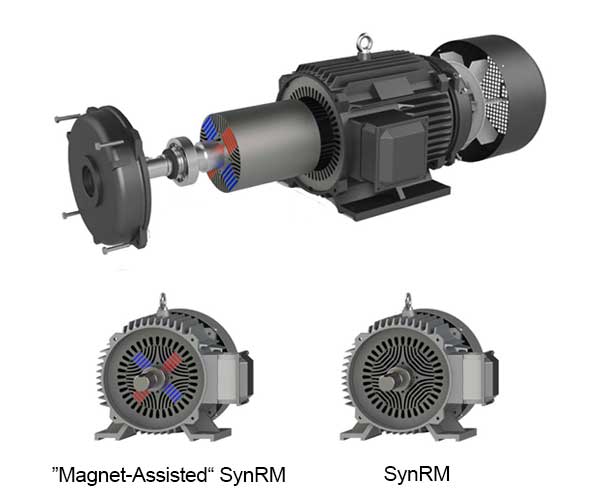

Magnet Assisted Synchronous Reluctance Motor
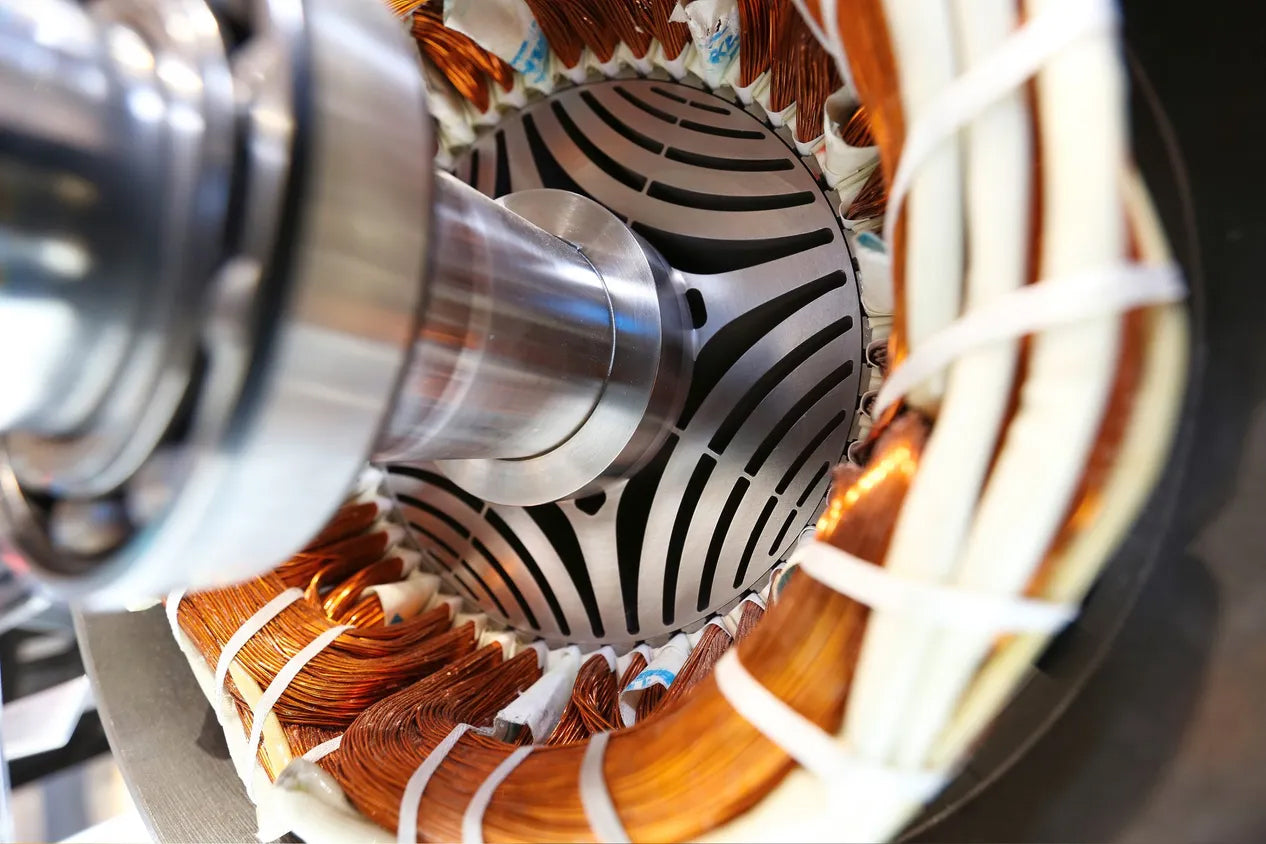
Synchronous Reluctance Motors (SynRM) are synchronous motors based on the "reluctance minimisation principle", where the torque (reluctance torque) generated by the special convex pole design of the rotor is used to drive the motor.
Helper magnet synchronous reluctance motors are developed on the basis of this technology, using high-temperature-resistant ferrite as a helper magnet material, which further improves performance, combining the reliability of asynchronous motors with the high performance of permanent magnet motors, making them a cost-effective and superior solution for efficient driving of industrial equipment.
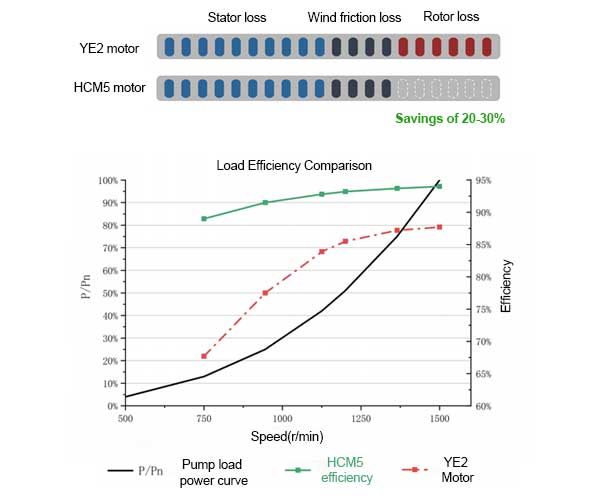
Energy Efficiency Comparison
HCM reluctance motors have no rotor losses compared to ordinary asynchronous motors because of their structure without squirrel cage windings, so the losses are reduced by 20% to 30%.
Under the condition of high speed of pump load, the efficiency of HCM5 reluctance motor is higher, the efficiency is more than 90%; while the efficiency of YE2 asynchronous motor is slightly lower, between 85% and 90%.
At low speeds, the efficiency of HCM5 motors can still reach more than 80 per cent, while the efficiency of YE2 asynchronous motors is only 20-30 per cent.
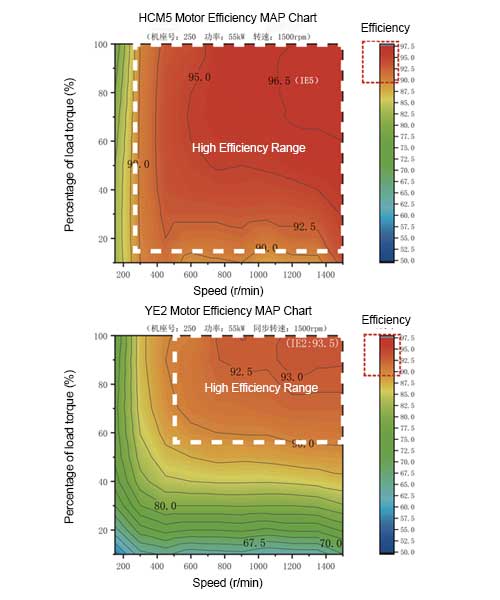
Efficiency Comparison Analysis
The pictures show the efficiency distribution of two motors, HCM5 and YE2, at different speeds and load torque conditions.
High efficiency region: HCM5 motors have a wider range of high efficiency region and higher efficiency (95.0%-96.5%), while YE2 motors have a relatively narrow high efficiency region and a slightly lower efficiency range (92.5%-93.0%).
Speed range: HCM5 motors can maintain more than 90% high efficiency in the speed range of 200 to 1500, while YE2 motors can maintain high efficiency only in the speed range of 500 to 1500.
Load torque: In the high efficiency region, HCM5 motors have a wider range of high efficiency load torque (20% to 100%), while YE2 motors can only maintain high efficiency at higher load torque (above 50%).
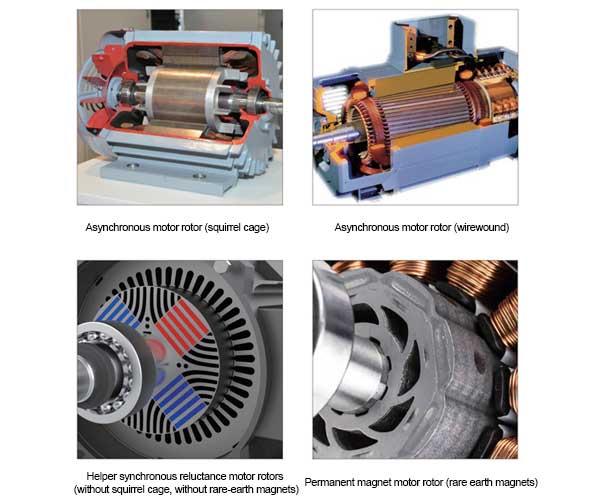

High Reliability And Economy Motor
Reliability: The magnet-assisted synchronous reluctance motor rotor has higher reliability due to the absence of squirrel cage and rare-earth permanent magnets, avoiding the risk of broken bars of squirrel cage rotor and demagnetisation of permanent magnets.
Economy: The main materials of magnet-assisted synchronous reluctance motor rotor are iron, copper and ferrite, which are relatively stable and economical, and do not contain expensive materials such as rare earth permanent magnets.
Subscribe to our emails
Be the first to know about new collections and exclusive offers.


